在线解析网址:https://astexplorer.net/
树结构
Node {
type: 'File',
program: Node {
type: 'Program',
start: 0,
end: 7,
loc: SourceLocation {
start: [Position],
end: [Position],
filename: undefined,
identifierName: undefined
},
sourceType: 'script',
interpreter: null,
body: [ [Node] ],
directives: []
},
comments: [] //注释
}type:"File" 代表整个文件
loc: 代表标识位 一般没用所以隐藏了
program:node节点 主要代码都在这
-body:node节点 把它当作html的body 所有可见的都在那
body下的xxx 比如VariableDeclaration: 这是节点类型啥的 后面介绍(后面遍历操作都是这些玩意)commets:代码里的注释
节点类型介绍(不用记,用网站解析)
VariableDeclaration:声明变量的时候 (var let const)
FunctionExpression:函数声明节点
BlockStatement:块(body)
Identifier:标识符(定义任何一个东西都会有个标识符 比如var a=1; a就是标识符)
BreakStatement:break中断语句 相应的还有ContinueStatement:continue继续语句
IfStatement:if判断语句
CallExpression:对象调用 比如console.log(); console对象调用log函数 另外computed为false
MemberExpression:对象成员表达式 比如console["log"] 另外computed为true
ObjectExpression: object对象 --- ArrayExpression: 数组 --- NewExpression:new
SwitchStatement:switch --- SwitchCase: case
暂时写这么多
ast解析库-四小工具介绍
@babel/parser 将js代码转成ast树
@babel/generator 将ast转回js代码
@babel/traverse 遍历ast节点
@babel/types 类型
parse js转ast树
const {parse} = require("@babel/parser")
var jscode=`
var a;
a=123
`
const ast_code = parse(jscode,{
sourceType:"module" //module是为了解析代码里有import而不会报错
})parse(js代码) 将js代码转成ast树了
文档:
https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/babel-parser
generator 转js
options介绍
name type default description(描述,机翻)
auxiliaryCommentAfter string 作为块注释添加到输出文件末尾的可选字符串
auxiliaryCommentBefore string 可选字符串,作为块注释添加到输出文件的开头
comments boolean true 输出注释
compact boolean or 'auto' opts.minified 设置为true可避免为格式添加空白
concise boolean false 设置为 "true "以减少空白(但不像opts.compact那样多)
decoratorsBeforeExport boolean 设置为 true在输出前打印装饰器export
filename string 在警告信息中使用
jsescOption object 只有当jsescOption.numbers(在v7.9.0中添加)存在时,jsesc才会应用于数字。你可以通过向它传递选项来定制jsesc。
jsonCompatibleStrings boolean false 设置为 "true "以运行带有 "json "的jsesc:"true "用于打印"\u00A9 "与"©"。
minified boolean false 输出是否应该被最小化
retainFunctionParens boolean false 保留函数表达式周围的括号(可用于改变引擎解析行为)。
retainLines boolean false 尝试在输出代码中使用与源代码中相同的行号(有助于保留堆栈跟踪)。
shouldPrintComment function opts.comments 该函数接收一个注释(字符串),如果该注释应该被包含在输出中,则返回true。默认情况下,如果opts.comments为true,或者opts.minified为false,并且注释包含@preserve或@license,注释就会被包含在内。
topicToken '%' or '#' 与Hack-pipe主题引用一起使用的令牌。当有任何TopicReference节点时,这是必须的。
const {parse} = require("@babel/parser")
const generator = require("@babel/generator").default
var jscode=`
var a;
a=123
`
const ast_code = parse(jscode,{
sourceType:"module" //module是为了解析代码里有import而不会报错
})
var js=generator(ast_code,{
//这里可以选择上面的optios
})traverse 遍历
比如js代码三行a=1; 就可以遍历他们俩Identifier NumericLiteral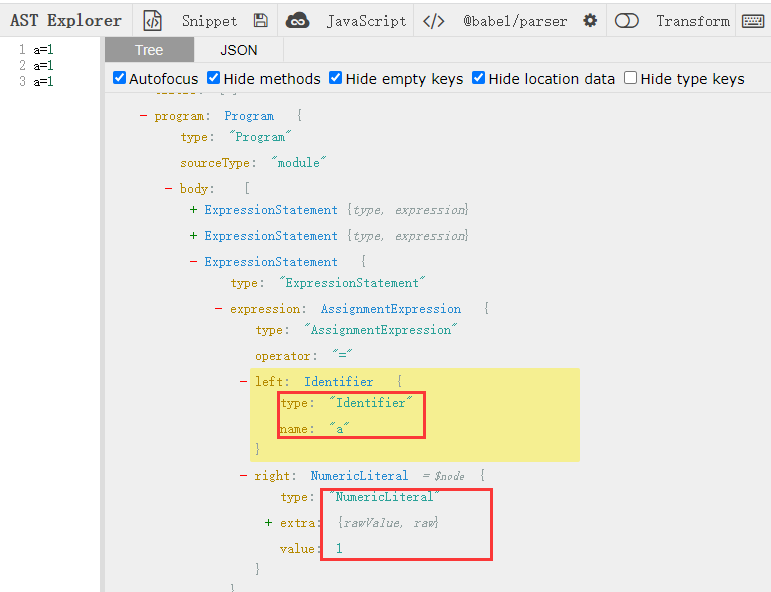
遍历 将a=1改成b=2
const ast_code = parse(jscode,{
sourceType:"module" //module是为了解析代码里有import而不会报错
})
const visitor={
"Identifier"(path){
path.node.name="b"
},
"NumericLiteral"(path){
path.node.value=2
}
}
traverse(ast_code,visitor)types.stringLiteral("shirmay");
得到一个node节点 { type: 'StringLiteral', value: 'shirmay' }
types.NumericLiteral(1);
得到一个node节点 { type: 'NumericLiteral', value: 1 }
types.valueToNode(11) 或者 types.valueToNode("11")
得到一个node节点 好像自动识别类型
isStringLiteral(node, opts) 判断node节点类型是否为stringxxx
其他杂记
path.parent 父级节点
path.parentPath 父级路径
findParent 向上遍历寻找父节点
result=path.findParent(function(result){return result.isVariableDeclaration()});
一直往上寻找父节点,传入一个回调函数 当满足回调函数要求返回,
返回的是一个node.path
find 向上遍历寻找父节点 包含当前节点
getFunctionParent 向上找函数
path.container 容器 path.key 容器索引 只有在数组时才有意义 inList
path.key 获取当前节点的key
path.getSibling(index) 获取同级节点path 要拿第几个传几
path.evaluate() //{ confident: true, deopt: null, value: 111 }
path.replaceWith(types.valueToNode("111")) //替换节点
//evaluate演示使用
var jscode=`
var a = 111;
var b = a;
`
Identifier(path){
if(path.node.name==="a"){
let ev=path.evaluate()
ev.confident && path.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(ev.value))
}
}
//结果输出
var a = 111;
var b = 111;path.scope作用域
function test(){
var i = 1;
var n = 2;
}
NumericLiteral(path){
console.log(path.scope.path+"")
}//结果会打印两次test函数及里面
path.scope.path 会返回当前作用域里的所有东西
path.scope.block 返回标识符作用域,返回node对象
path.scope.getBinding(标识符) 获取标识符的绑定 比如下面的函数,遍历 FunctionDeclaration 返回node对象 可以getBinding("a")
binding.referencePaths.length返回(标识符)引用次数 ,binding.references返回对象(标识符)引用次数 referenced是否在其他地方引用 还有个hasBinding查询是否有绑定
binding.referencePaths获取上面绑定标识符的引用路径(数组 path) 好东西
scope.rename("a","b")改当前作用域名字
scope.getOwnBinding 获取当前节点自己的绑定,不包含父级作用域中的标识符
function test(a){
a=11+a;
a++;
return a;
}scope.rename("a","b") 相当于修改作用域里的变量名
scope.dump() 打印当前作用域的一些信息
scope.getAllBindings() 返回所有的标识符 对象
scope.getBindingIdentifier('标识符') 获取标识符本身
还原小小小案例
先上准备代码
const parse = require("@babel/parser"); //解析为ast
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default;//遍历节点
const types = require('@babel/types');//类型
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default;//ast解析为代码
// const fs = require("fs");//文件读写
//读取js文件
// const jscode = fs.readFileSync(
// './demo.js', {
// encoding: 'utf-8'
// }
// );
jscode=`
`
let ast = parse.parse(jscode);//js转ast
let visitor={}
traverse(ast, visitor);
let {code} = generator(ast,opts = {jsescOption:{"minimal":true}})
console.log(code);
//fs.writeFile('./demoNew.js', code, (err) => {
//});打开 ast在线解析工具
1:经典的16进制和Unicode还原
代码长这样的:
jscode=`
var t =(new window['\x44\x61\x74\x65'])["\u0067\u0065\u0074\u0054\u0069\u006d\u0065"]()
var t2 = 0x0;
`
let ast = parse.parse(jscode);//js转ast
let visitor = {
"StringLiteral|NumericLiteral"(path) {
let node = path.node;
delete node.extra;
}
}
//数字与字符还原
traverse(ast, visitor);
let {code} = generator(ast)
console.log(code)
//结果
//var t = new window['Date']()["getTime"]();
//var t2 = 0;用ast在线解析工具很明显看到16进制和字符串的内容,遍历字符串和数字,删除extra就好了。
2:字符串相加
window"ev" + "al"
选中两个相加的,类型为BinaryExpression 这种只需要遍历它 加个判断字符串 然后left+right就可以了
简单的两个字符串相加
jscode = `
window["ev" + "al"]("deb"+"ugger")
`
let visitor = {
"BinaryExpression"(path) {
let node = path.node;
//只要判断左边和右边是不是都是字符串 可以再判断下中间的符号是不是+号
if (node.left.type === "StringLiteral" && node.right.type === "StringLiteral") {
//替换节点
path.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(node.left.value + node.right.value))
}
}
}多个加号的
jscode = `
window["ev" + "al"]("de"+"b" + "u"+"gg" + "er")
`
let visitor = {
"BinaryExpression":{
exit(path) {
let node = path.node;
if (node.left.type === "StringLiteral" && node.right.type === "StringLiteral") {
path.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(node.left.value + node.right.value))
}
}
}
}//因深度优先 后进先出 所以用exit去遍历
3:美化对象调用的中括号为"点"
let jscode = `
console['log']("123")
console.log("123")
`
let visitor = {
"MemberExpression"(path) {
let node = path.node;
if (node.property.type==="StringLiteral"){
node.computed=false;
node.property.type="Identifier";
node.property.name=node.property.value;
delete node.property.extra;
}
}
}4:减少中间商-删除没使用的变量和多余的传递变量
let jscode = `
let a=333;
b=a;
let c=a;
d=b+2;
console.log(d);
function test(){
let a=999;
let b=a+2;
return b;
}
`
let visitor = {
"VariableDeclarator"(path) {
let {node} = path;
if (path.type === "VariableDeclarator") {
let left = node.id;
let right = node.init;
//没有右边说明只定义了,没赋值。比如 var hliang;
if(!right||!right.type)return;
let bind = path.scope.getBinding(left.name);
// console.log(left.name,bind.references)
// 获取当前作用域标识符的引用次数,如果等于0说明声明了变量没有使用,那就直接删除。
if(bind.references===0){
console.log(left.name,"作用域引用次数为0,直接删除")
path.remove()
return;
}
// 如果右边等于字符串 数字 或者标识符Identifier就继续操作
if (right.type === "NumericLiteral" || right.type === "StringLiteral" || right.type === "Identifier") {
let referencesNums=0;
for(let item of bind.referencePaths) {
// console.log(left.name,":",right.name,right.type,right.value,item.node.type,item.node.name)
if(right.type==="NumericLiteral"){
item.node.type="NumericLiteral"
item.node.value=right.value
referencesNums+=1;
}else if(right.type==="StringLiteral"){
item.node.type="StringLiteral"
item.node.value=right.value
referencesNums+=1;
}else if(right.type==="Identifier"){
item.node.name=right.name;//标识符重命名
referencesNums+=1;
}
if (referencesNums===bind.references){//若绑定的每个路径都已处理 ,则移除当前路径
path.remove();//删除路径
}
}
}
}
}
}
//结果:
// c 作用域引用次数为0,直接删除
// b = 333;
// d = b + 2;
// console.log(d);
//
// function test() {
// let b = 999 + 2;
// return b;
// }这个有个注意点(bug),就是在这个作用域 同级函数里面 变量没声明的话 会直接替换掉,比如
let jscode = `
let a=333;
b=a;
function test(){
let a=999;
b=a+2;
return b;
}
`//上面的代码test函数里面的return b就会被替换成return 333。
还原小案例:
数美滑块和动态post参数,key
描述:听说数美现在的混淆是个改版ob,一个des(ecb模式) 加密 这里不讲,只讲ast部分,通过ast 还原了大数组和Object对象 想要获取动态的key,这两个是必须的,不定时天数换个小版本,目前写的145-158(2022/6/14最新)版本可以成功解析获取key,之前的版本还要继续写匿名函数实参形参替换才能获取key。 通用太难写了。
1.visitor1,最经典的还原Unicode和16进制
let visitor1 = {
// 最经典的,把Unicode和16进制的字符串数字还原
"NumericLiteral|StringLiteral"(path) {
delete path.node.extra;
},
// 获取自执行函数,第一个自执行会改变大数组的顺序,所以这里遍历一下把自执行函数的代码保存给全局 后面运行
"CallExpression"(path) {
let {node} = path;
if (!node.callee || node.callee.type !== "FunctionExpression") return;
if (!node.arguments || node.arguments.length !== 2) return;
if (node.arguments[0].type !== "Identifier") return;
// 修改大数组的是一个匿名函数,这里加个感叹号让他语法没问题
// 转ast再转js代码 使用了压缩,防止toString检测导致内存爆破卡死。
let changeAst = parser.parse("!" + path.toString());
let ChangeArrayOrder = generator(changeAst, opts = {"compact": true}).code;
console.log("改变数组顺序的自执行代码:", ChangeArrayOrder)
global["ChangeArrayOrder"] = ChangeArrayOrder;
path.remove();
}
}在最外层那个自执行会改变大数组的顺序,通过ast 一大堆判断 得到正确的匿名函数,再保存到全局(node里全局用global)等下次和大数组,解密函数执行后执行。有的会有toString检测,直接格式化。
2.还原通过函数传入一个数字来的到结果(大数组解密)
这里visitorArray通过遍历Var类型加一大堆判断 比如 var a = ["1","aa"],再往上找函数,如果找不到说明就是最外层定义的数组,再把大数组保存到全局,再通过数组的父级path来得到解密的函数 比如"_0x1e4a2f(0x614)"得到一个字符串_0x1e4a2f就是解密函数,现在获取整一个_0x1e4a2f函数的内容,并且保存到全局。
还有个快速写的思路,就是通过最外层的body来写,但这个太多局限性 仅用于单个不会变的js解混淆
然后往下看。
//解决大数组
let visitorArray = {
"VariableDeclarator"(path) {
let {id, init} = path.node;
// 判断var右边是不是数组类型
if (!init || init.type !== "ArrayExpression" || init.elements.length < 1) return;
// 获取作用域
let binding = path.scope.getBinding(id.name);
// 如果作用域的引用次数等于0,就说明不是,那就删除并且返回
if (binding.references === 0) {
path.remove;
return
}
// every 遍历数组 判断全部的成员的是否为StringLiteral
if (init.elements.every(element => element.type === "StringLiteral")) {
//获取父级函数,如果没有就说明是最外层定义的数组
let funcName = path.getFunctionParent();
if (funcName === null) {
console.log("大数组名字应该是:", id.name)
global["largeArray"] = path.toString();
path.remove;
// 父级作用域传给另外一个函数操作
getDecName(path.parentPath)
} else {
// 获取最后一个返回的函数名 和父级函数名对比,如果一样 就eval
let lastElement = funcName.node.body.body.at(-1)
if (!lastElement.argument || !lastElement.argument.callee) return;
if (lastElement.type !== "ReturnStatement" && lastElement.argument.callee.name !== funcName.node.id.name) return;
console.log("大数组名字应该是函数名:", funcName.node.id.name)
let largeArrayAst = parser.parse(funcName.toString());
global["largeArray"] = generator(largeArrayAst, opts = {"compact": true}).code;
// 父级作用域传给另外一个函数操作 获取解字符串函数
getDecName(funcName.parentPath)
// 移除掉大数组
funcName.remove()
}
}
},
}
function RecursiveAssignment(path, pPathString) {
eval(global["largeArray"]); //加载大数组
eval(pPathString); //加载解密函数
eval(global["ChangeArrayOrder"])
if (!pPathString || !global["largeArray"] || !global["ChangeArrayOrder"]) {
throw "有些没解析全,退出"
}
// 递归函数,因为他的引用又是一个赋值新变量操作
//代码长这样子的: var _0x1e4a2f = _0x4a9d; console.log(_0x4a9d(100));
let {name} = path.node.id;
let binding = path.scope.getBinding(name);
for (p of binding.referencePaths) {
let pPath = p.parentPath;
let {node} = pPath;
if (node.type === "VariableDeclarator") {
let leftName = node.id.name;
let rightName = node.init.name;
// console.log("似乎要把解密函数"+rightName+"赋值给", leftName);
// // 先改成解密函数的名字,
pPath.scope.rename(leftName, rightName);
RecursiveAssignment(pPath, pPathString);
// // 移除掉赋值新变量名
pPath.remove();
}
//console.log(pPath.toString());
// 判断是调用函数,替换节点
if (node.type === "CallExpression" && node.arguments.length === 1 && && node.arguments[0].type === "NumericLiteral") {
let pPathCode = pPath.toString();
let result = eval(pPathCode)
// console.log(pPathCode, ":", result);
pPath.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(result))
}
}
}
// 获取解密函数代码
let getDecryption = {
"FunctionDeclaration"(path) {
// 判断函数是不是需要传两个参数
let {node} = path;
let {body} = node;
if (!node.params || node.params.length !== 2) return;
if (!body || !body.body) return;
let lastReturn = body.body.at(-1)
if (lastReturn.type !== "ReturnStatement" || !lastReturn.argument || !lastReturn.argument.expressions) return;
let lastCall = lastReturn.argument.expressions.at(-1)
if (lastCall.type !== "CallExpression" || lastCall.arguments.length !== 2) return;
let name = node.id.name;
console.log("解密函数的名字是:", name);
let decryAst = parser.parse(path.toString());
let decryCode = generator(decryAst, opts = {"compact": true}).code;
RecursiveAssignment(path, decryCode);
// 移除解字符串函数
path.remove();
}
}
var getDecName = (path) => {
// 这个函数 通过大数组的作用域传入同级作用域 来获得解密函数
let {scope} = path;
scope.traverse(scope.block, getDecryption);
}获取到了解密的函数后 通过遍历作用域引用路径来替换节点解大数组,这里RecursiveAssignment是一个递归函数,因为他把解密函数赋值给新的一个函数了,那么获取绑定标识符就要改成新的。所以我先把赋值的及它的作用域名字全改成解密函数的名字,用了一个递归 传新标识符过来重新走一遍解密。它赋值的次数还挺多的
像楼下这图还能翻10多张。。。
3.visitor2 优化加减乘除操作和解对象
比如:这种代码 "-0x7 0xe3 + -0x1 0xaae + -0x2 * -0x872"
和这种代码// var _0x4b4e24 = {
// "Xpwku": "<div id=\"",
// "WuoUF": function (_0x3e6935, _0x10f1b1) {return _0x3e6935 + _0x10f1b1;}// }
加减乘除的看代码注释吧。讲讲解对象。
一开始还是一系列判断是否为Object,再新建个新对象,把解析的成员node全部丢给它,后续引用路径来和它node里面的东西判断
根据多个对象结合 对象成员的返回值来看,一共两大类,三小类
先if判断是字符串还是函数,字符串没啥说的直接替换,如果是函数,再根据它的返回类型 继续做判断
返回类型也一共就那三小类
折叠的代码比较好看,建议折叠代码然后根据上面说的来看
三小类介绍:
logical和binary两个类型好像都差不都,就是logical的opertor是"||" ,这两个直接套娃替换
CallExpression的话,好像都是第一个参数是函数,然后剩下参数当函数调用的参数
let visitor2 = {
// 优化加减乘除操作
"BinaryExpression": {
exit(path) {
let {node} = path;
let {left} = node;
let {right} = node;
if ((left.type === "UnaryExpression" || left.type === "NumericLiteral") && (right.type === "UnaryExpression" || right.type === "NumericLiteral")) {
let leftValue;
let rightValue;
if (left.type === "NumericLiteral") {
leftValue = left.value
} else {
if (!left.argument.value) return;
if (left.operator === "-") {
leftValue = -left.argument.value
}
}
if (right.type === "NumericLiteral") {
rightValue = right.value
} else {
if (!right.argument.value) return;
if (left.operator === "-") {
rightValue = -right.argument.value
}
}
if (!leftValue) return;
//console.log(leftValue, node.operator, rightValue);
path.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(path.evaluate(leftValue + node.operator + rightValue).value));
}
}
},
//解对象
"VariableDeclarator"(path) {
// 其他的话对局部数组做的,比如代码:
// var _0x4b4e24 = {
// "Xpwku": "<div id=\"",
// "WuoUF": function (_0x3e6935, _0x10f1b1) {return _0x3e6935 + _0x10f1b1;}}
let {node} = path;
let {id, init} = node;
if (!init || init.type !== "ObjectExpression") return;
if (!init.properties || init.properties.length < 1) return;
let Array2Name = id.name;
//新建一个对象。把原来的对象右边(value)保存为Node
let NewObject = {};
for (v of init.properties) {
NewObject[v.key.value] = v.value;
}
let binding = path.scope.getBinding(Array2Name)
// 新建一个操作次数,如果数组的引用节点都操作了的话 次数加一 如果等于所有次数,就说明全修改了,可以删除定义的节点了
let modificationNum=0
for (p of binding.referencePaths.reverse()) {
// 此时的p是数组名称,要父级path才有成员名
let pPath = p.parentPath;
let {node} = pPath;
// 获取调用数组成员的名字,再放进新对象查一下是字符串还是函数,如果是函数,还要往上找父级path,类型才是CallExpression
// 如果没有property 说明不是调用某个成员,可能是要调用或赋值自己给其他的
if (!node.property) return;
let keyName = node.property.value;
let rightNode = NewObject[keyName]
if (!NewObject[keyName]) return
if (rightNode.type === "StringLiteral") {
// console.log("旧代码111", pPath.toString())
pPath.replaceWith(types.valueToNode(rightNode.value));
modificationNum+=1
// console.log("新代码111", pPath.toString())
// console.log("-------------------")
} else if (rightNode.type === "FunctionExpression") {
// 此时这里的pPath.node为_0xa7a3b2["JHTcH"] 还要上一级才会有arguments的东西
node = pPath.parentPath.node;
let {parentPath} = pPath
if (node.type !== "CallExpression") return;
if (!rightNode.body || !rightNode.body.body) return;
let bodyResult = rightNode.body.body[0];
if (bodyResult.type !== "ReturnStatement") return;
let {arguments} = node;
//BinaryExpression 就是长这样的代码 return _0x398914 == _0x5433f6;
if (bodyResult.argument.type === "BinaryExpression") {
let {operator} = bodyResult.argument
// 只有一个参数,说明是判断类型的,右边固定
if (arguments.length === 1) {
parentPath.replaceWith(types.binaryExpression(operator, node.arguments[0], bodyResult.argument.right))
modificationNum+=1
} else if (arguments.length === 2) {
// console.log("旧代码222", pPath.toString())
parentPath.replaceWith(types.binaryExpression(operator, node.arguments[0], node.arguments[1]))
modificationNum+=1
// console.log("新代码222", parentPath.toString())
// console.log("-------------------")
}
}else if(bodyResult.argument.type==="LogicalExpression"){
parentPath.replaceWith(types.logicalExpression("||", node.arguments[0], node.arguments[1]))
modificationNum+=1
}else if (bodyResult.argument.type === "CallExpression") {
if (node.arguments.length >= 1) {
// console.log("旧代码", pPath.parentPath.toString())
pPath.parentPath.replaceWith(types.callExpression(node.arguments[0], node.arguments.slice(1)));
modificationNum+=1
// console.log("新代码", pPath.parentPath.toString())
// console.log("-------------------")
}
}
}
}
if(modificationNum===binding.referencePaths.length){
// console.log("删除了一个小数组。")
path.remove()
}
}
}4.获取动态的数据
// 获取动态post参数和加密的key
let key_dict=[];
let visitor3={
"AssignmentExpression"(path){
let {node}=path;
let {left,right}=node;
if(!left.property||left.property.type!=="StringLiteral")return
if(!right||!right.arguments||right.arguments.length!==2)return;
if(right.arguments[1].type!=="StringLiteral"||right.arguments[1].value.length!==8)return;
// console.log(left.property.value,right.arguments[1].value)
key_dict.push([left.property.value,right.arguments[1].value])
}
}
这不是我蔡老板写的代码,怎么被你粘过来了
我承认在csdn看过jia666的ast和蔡老板的某些小节思路,但是这些代码都是tmd我一个一个敲得,目的是为了还原某美的动态参数,这个成品目前还可以还原它